
pediatric clinical examination pdf
Pediatric clinical examination is a specialized process requiring skill and adaptability. It begins with a detailed history and progresses through physical assessment, ensuring accurate diagnoses and effective care.
1.1 Importance of Pediatric Clinical Examination
The pediatric clinical examination is crucial for diagnosing and managing conditions in children. It combines a thorough medical history with a physical assessment, forming the cornerstone of pediatric care. A detailed history helps identify symptoms and developmental milestones, while the physical exam provides insights into growth, development, and potential abnormalities. This process ensures early detection of illnesses, guiding timely interventions. Effective communication and age-appropriate techniques are essential to make children comfortable, reducing anxiety and building trust. The fundamentals of a thorough history and physical examination remain unchanged, even as diagnostic tools evolve. These skills are vital for pediatricians to deliver evidence-based, compassionate care.
1.2 Evolution of Pediatric Clinical Practice
Pediatric clinical practice has evolved significantly over the years, adapting to advancements in medical knowledge and technology. Historically, the focus was on infectious diseases and basic care, but modern practice integrates genetics, immunology, and advanced imaging. The development of vaccines and antibiotics revolutionized treatment, reducing mortality rates. Today, there is greater emphasis on preventive care, early intervention, and holistic approaches. Guidelines from organizations like the American Academy of Pediatrics provide evidence-based standards, ensuring consistent and high-quality care. Continuous professional development and the integration of new diagnostic tools, such as MRI and ultrasonography, have further enhanced clinical practice, enabling more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans for children. These advancements reflect a commitment to improving pediatric health outcomes globally.
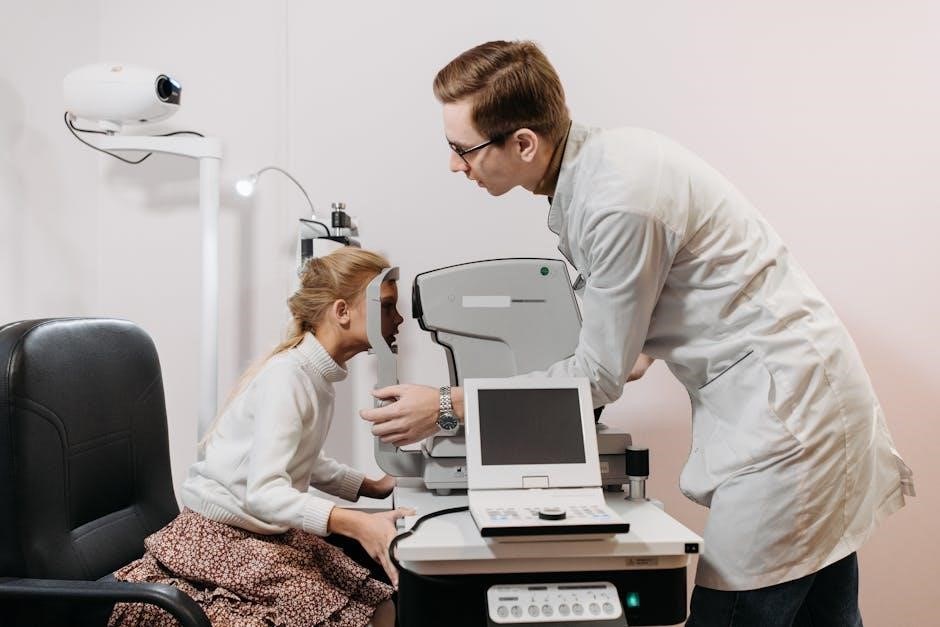
Components of Pediatric Clinical Examination
Pediatric clinical examination involves a comprehensive medical history and a detailed physical assessment. These components are essential for accurate diagnosis and effective patient care in pediatric settings.
2.1 Medical History and Its Significance

A thorough medical history is the cornerstone of pediatric clinical examination. It involves gathering detailed information about the child’s chief complaint, birth history, developmental milestones, immunization status, and past illnesses. This process helps identify potential health issues early and informs the physical examination. Parents or guardians often provide this history, requiring clear communication and empathy. The medical history guides diagnostic decisions and treatment plans, making it essential for accurate patient care. Its significance lies in its ability to uncover subtle clues that may not be apparent during the physical exam, ensuring comprehensive and personalized care for children.
2.2 Physical Examination Techniques
Physical examination techniques in pediatrics require skill and adaptability to the child’s age and developmental stage. The process often begins with observation, followed by a systematic head-to-toe assessment. Techniques may involve the use of toys or distractions to make the child comfortable. Vital signs, growth parameters, and developmental milestones are key components. The examination should be gentle and non-invasive, ensuring the child’s cooperation. Special attention is paid to signs of illness, such as respiratory distress or abdominal tenderness. The physical exam complements the medical history, providing essential clues for diagnosis and guiding further investigations. A calm and patient approach is crucial to ensure accuracy and build trust with the child and family.
Special Considerations in Pediatric Exams

Pediatric exams require tailored techniques and adaptability to age-specific needs. Children’s unique physiology and developmental stages demand a gentle, child-friendly approach, ensuring accurate assessments and effective care.
3.1 Age-Specific Examination Techniques
Age-specific techniques are crucial in pediatric exams, as children’s anatomy and behavior vary significantly. Infants require gentle handling and attention to vital signs, while toddlers benefit from play-based assessments to minimize anxiety. School-aged children can follow instructions, enabling more structured examinations. Adolescents need privacy and sensitivity, involving them in the process. Each age group demands a tailored approach to ensure accurate diagnoses and build trust. Techniques must adapt to developmental stages, ensuring comfort and cooperation. This age-specific care enhances the effectiveness of the clinical examination, making it a cornerstone of pediatric practice.
3.2 Communication Strategies with Children
Effective communication is vital in pediatric exams to build trust and cooperation. Using simple, age-appropriate language helps children understand the process. Non-verbal cues like smiles and gentle gestures can reduce anxiety. Involving parents or caregivers in the conversation provides reassurance and context. Explaining each step before performing it ensures transparency and prepares the child. Cultural sensitivity and adaptability are essential, as communication styles may vary. Active listening and patience are key to addressing concerns. These strategies foster a positive environment, making the examination process smoother and more effective for both the child and healthcare provider.

Diagnostic Tools and Decision-Making
Diagnostic tools like imaging and lab tests guide decision-making in pediatric care, integrating clinical findings to ensure accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
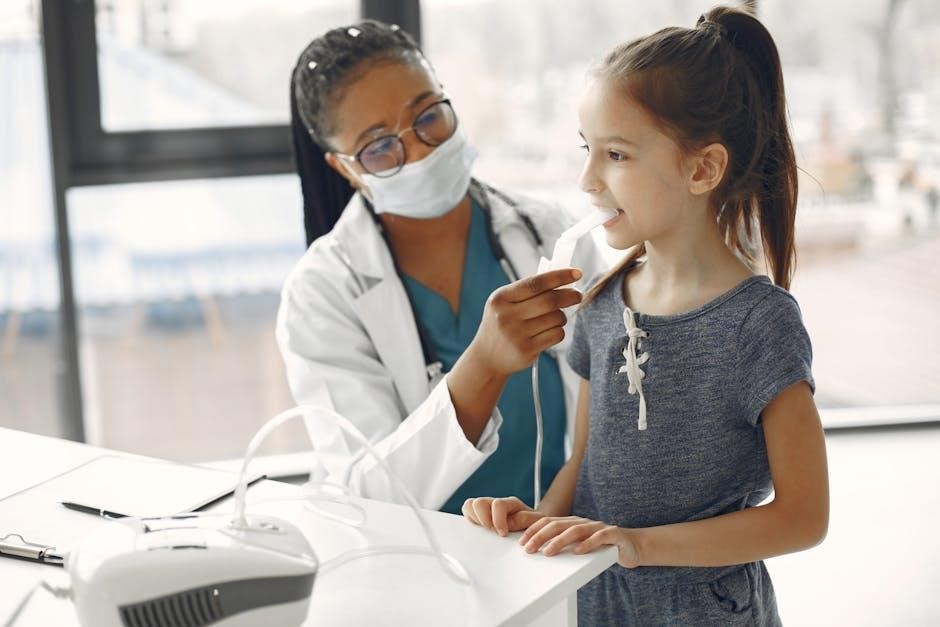
4.1 Role of Imaging in Pediatrics
Imaging plays a crucial role in pediatric diagnostics, offering insights into complex conditions. Techniques like MRI and echocardiography are invaluable for assessing brain, abdominal, and cardiac abnormalities. Advanced imaging tools provide detailed visualization, aiding in the diagnosis of fractures, infections, and congenital defects. They complement clinical findings, ensuring precise care plans. Regular updates in imaging technologies enhance diagnostic accuracy, making them indispensable in modern pediatric practice.
4.2 Laboratory Tests and Interpretations
Laboratory tests are essential in pediatric diagnostics, complementing clinical findings. Common tests include complete blood counts, blood chemistry, and urinalysis, aiding in identifying infections, metabolic disorders, and organ dysfunction. Accurate interpretation requires consideration of age-specific reference ranges, as normal values vary in children. For instance, liver enzyme levels naturally decrease with age, while kidney function parameters mature over time. Specialized tests, such as stool analyses or allergy panels, are used for specific conditions. Integrating lab results with clinical observations ensures precise diagnoses and tailored treatment plans, emphasizing the importance of laboratory investigations in pediatric care.

Resources for Pediatric Clinical Examination
Comprehensive guides like “Pediatric Clinical Examination Made Easy” and “Santhosh Kumar Paediatric Clinical Examination” offer detailed insights, available as PDF downloads for convenient access to practical skills.
5.1 Recommended Textbooks and Guides
Essential resources for pediatric clinical examination include textbooks like Pediatric Clinical Examination Made Easy and Guide to Paediatric Clinical Examination by S.S. Chin. These guides provide detailed, evidence-based approaches to assessing children. Santhosh Kumar Paediatric Clinical Examination is another valuable resource, offering practical insights into examination techniques. Additionally, The Rational Clinical Examination and Fast Facts Handbook for Pediatric Primary Care are highly recommended for their focus on diagnostic accuracy and decision-making. These textbooks are widely available in PDF formats, making them accessible for healthcare professionals seeking to enhance their clinical skills in pediatric care. They emphasize the importance of a thorough history, physical examination, and logical conclusions.
5.2 Online Resources and PDF Manuals
Several online resources and PDF manuals are available for pediatric clinical examination. Notable ones include Pediatric Clinical Examination Made Easy and Santhosh Kumar Paediatric Clinical Examination, both accessible as free PDF downloads. These manuals provide practical guidance on examination techniques, history-taking, and diagnostic decision-making. Additionally, Guide to Paediatric Clinical Examination by S.S. Chin and The Rational Clinical Examination are highly recommended for their comprehensive insights. These resources are often available on academic databases, medical websites, and platforms offering open-access materials. They are invaluable for healthcare professionals seeking to refine their pediatric clinical skills and stay updated with evidence-based practices.
Best Practices in Pediatric Clinical Care

Best practices emphasize thorough history-taking, complete physical exams, and logical deductions. Evidence-based guidelines and effective communication ensure high-quality, patient-centered care in pediatric settings.
6.1 Evidence-Based Clinical Guidelines
Evidence-based clinical guidelines form the cornerstone of pediatric care, ensuring decisions align with current research. These guidelines, regularly updated, address diagnosis, treatment, and management of various pediatric conditions. They emphasize the importance of a thorough clinical examination, including history-taking and physical assessment, to guide accurate diagnoses. By following these guidelines, healthcare providers minimize variability and improve patient outcomes. Furthermore, they facilitate consistency across different healthcare settings, ensuring that all children receive standardized, high-quality care. Adherence to these guidelines also supports continuous professional development, as they often incorporate new advancements in pediatric medicine. Ultimately, evidence-based guidelines enhance the reliability and effectiveness of pediatric clinical practice.
6.2 Continuous Professional Development
Continuous professional development (CPD) is essential for healthcare providers in pediatric care, ensuring they stay updated with the latest advancements and best practices. Regular engagement with educational resources, such as pediatric clinical examination PDFs, helps practitioners refine their skills. Workshops, conferences, and online courses are vital for enhancing clinical expertise. Additionally, self-directed learning through textbooks and guidelines ensures providers are well-informed. CPD fosters a culture of lifelong learning, enabling professionals to adapt to evolving medical knowledge and improve patient outcomes. By prioritizing professional growth, pediatric clinicians can deliver evidence-based, compassionate care tailored to children’s unique needs, ultimately enhancing their competence and confidence in clinical practice.